Maize – what a versatile crop!
April 2020
Maize is the most common staple for South Africa and most of the world. Maize contains approximately 72% starch, 10% protein, and 4% fat, supplying a substantial amount of energy for humans and animals. Maize can be used in various industries for the production of food and industrial products, including starch, sweeteners, oil, beverages, glue and industrial alcohol.
This article focuses on our local maize products as well as some common maize by-products used in other industries.
LOCAL MANUFACTURING OF MAIZE PRODUCTS
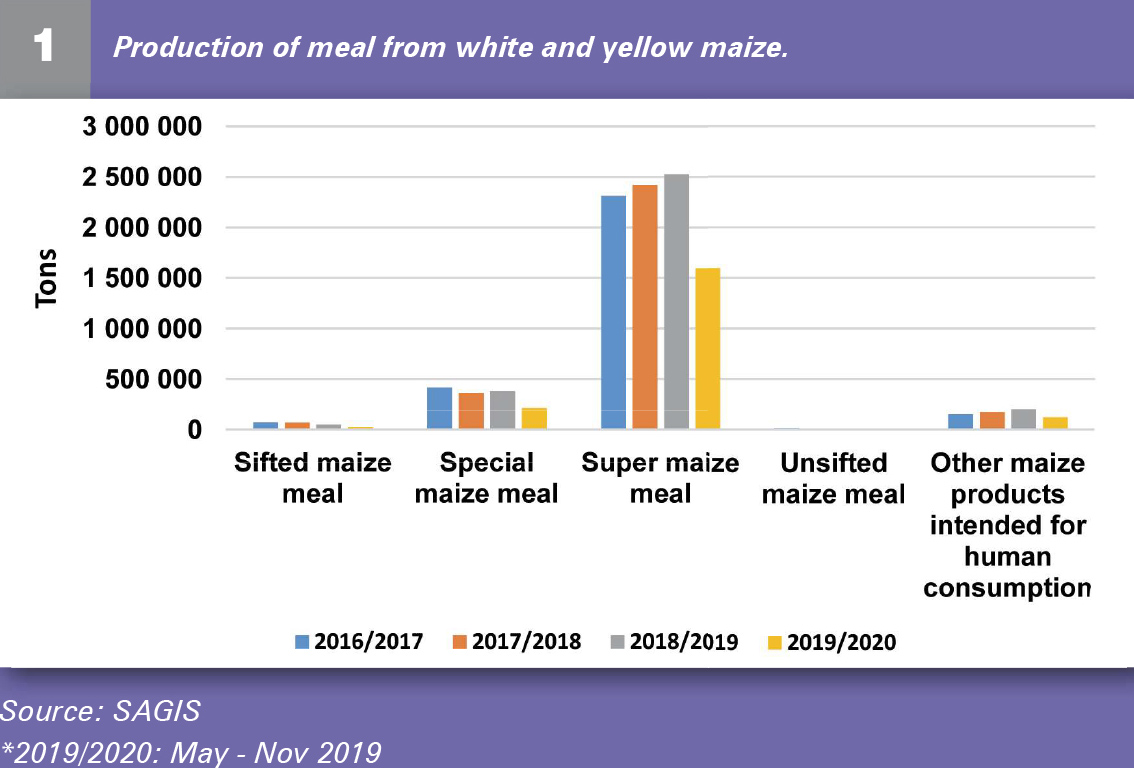
Figure 1 indicates different kinds of maize meal produced from white and yellow maize in South Africa. Most of the maize over the past five years was used to produce super maize meal.
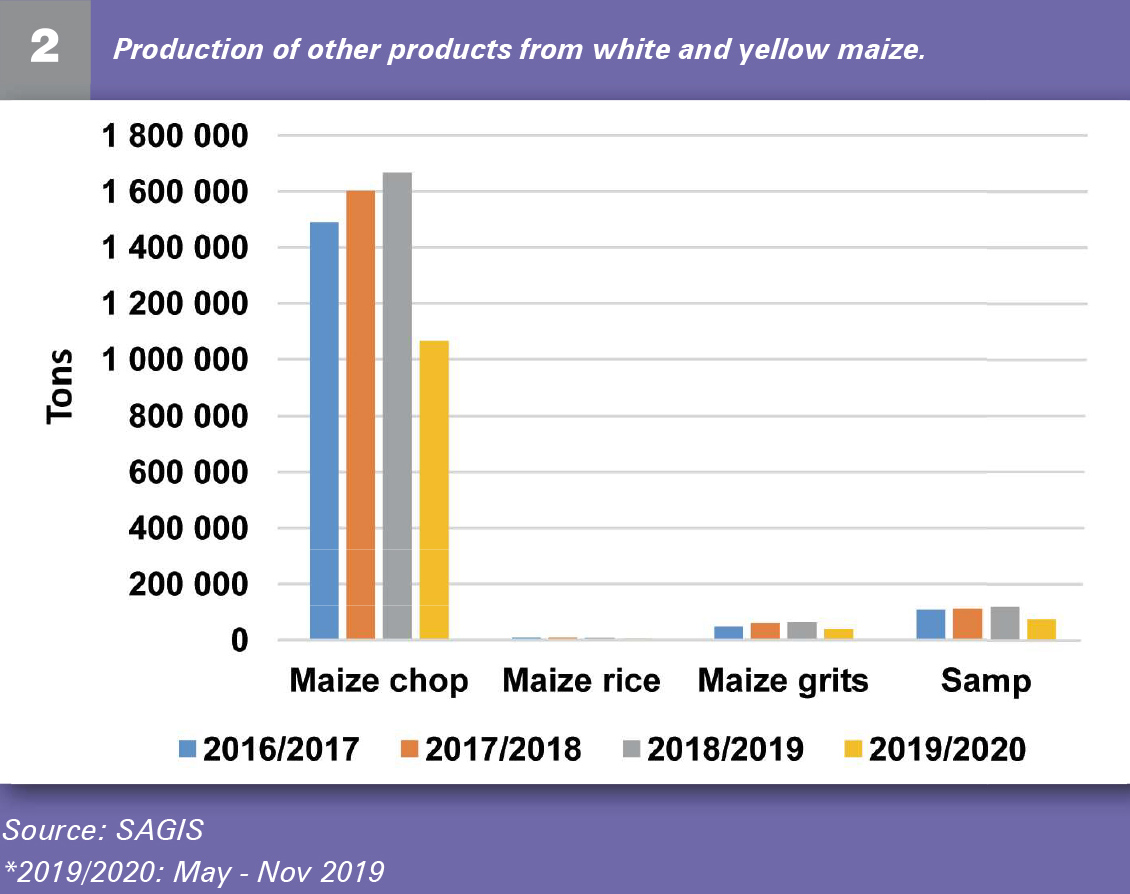
Figure 2 indicates production of other maize products in the South African market, which includes maize chop, maize rice, maize grits and samp, most of which is made from white maize. Over the past five years, South Africa produced a great amount of maize chop that goes into the animal feed industry.
LOCAL EXPORT MARKET
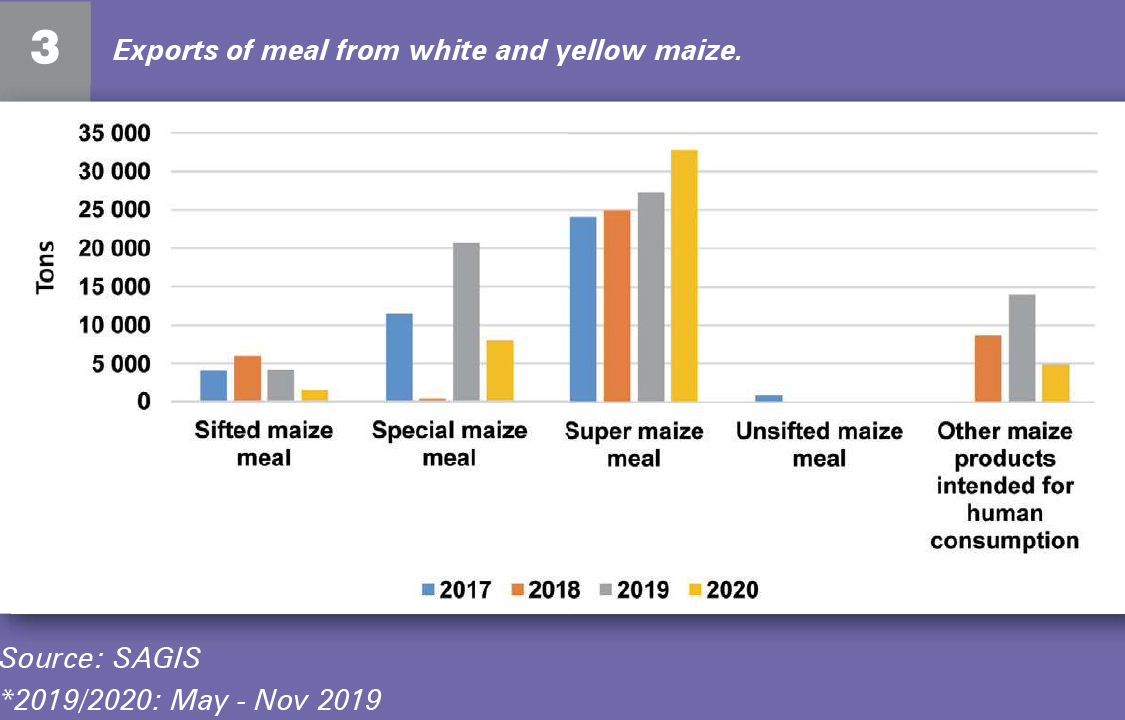
Figure 3 shows maize meal exports over the past five years, most of which goes into the African market. South Africa imports a negligible amount of meal.
MAIZE BY-PRODUCTS
Animal feed
- Maize gluten meal: Is a by-product of the manufacture of maize starch by the wet-milling process. Corn gluten meal is a protein-rich feed, used as a source of protein, energy and pigments for livestock species including fish.
- Maize fibre: Cellulosic fraction of the maize grain, rich in carbohydrates, easily digestible. Product of the manufacture of corn starch. Used in cattle breeding and oil cake manufacturing industry.
- Oil cake: After expelling oil from dry maize germs, the residue is corn oil cake. As it has a substantial amount of fat and protein, it is used as a major ingredient in the cattle feed industry.
Food industry
- High maltose maize syrup: Is a food additive used as a sweetener and preservative. Used in producing ice creams, confectionary and baked goods.
- Maize oil: Is extracted from the germ of maize. Used in the food industry as a cooking medium.
- Liquid glucose: Maize syrup or glucose syrup are synonyms and are usually manufactured by subjecting starch to high temperature in the presence of acid. Used in manufacturing food products like jam, jellies, chewing gums, canned fruits.
- Special maize starch: Is the starch derived from the maize. The starch is obtained from the endosperm of the kernel. Commonly used in thickening sauces or soups, and in making maize syrup and other sugars.
- Dextrose monohydrate: Is a white crystalline powdered sugar obtained from the complete hydrolysis of maize starch. It is used as a sweetener, a fermentation substrate, a wetting agent or in confectionery, bakery, snacks, beverages and dairy products.
Textile and paper industries
- Sayatex: Is an oxidized starch derived from maize. The film produced from sayatex is strongly adherent, continuous and clear. It is used for surface sizing of paper and yarn.
- Native maize starch: Is a cereal starch, which has a low ash and protein content. It is used in the textile finishing operation to change stiffness, feel or handle of the fabrics, to modify the appearance by filling the interstices of the weave and to add weight. Also used in the paper industry.
- Fabrilose: Modified, thin, boiling starch, used in textile sizing.
- Dextrins: Are normally prepared by roasting starch in the presence of acid which materially changes the character and properties of starch. They are used in foundries, distemper and textiles.
- Sayafied: Esterfied starch plays an important role in the manufacture of gypsum wallboard, protecting the gypsum crystals that form the bond between the gypsum core and the paper. Used in the paper industry and textile sizing industry.
Pharmaceutical industry
- Dextrose anhydrous: Is used in intravenous injections vital for preventing dehydration.
- Starch ip/bp: Is specially manufactured for the pharmaceutical industry. The major use of starch in pharmaceutical formulation is as a binder and filler for tablets and capsules.
- Maize steep liquor: Or CSL is a by-product of the wet milling of maize. It contains much of maize’s soluble protein, carbohydrates and minerals. It has a vital function in production of penicillin and other antibiotics.
Multiple industries
- Sorbitol: Is a sugar alcohol, which the human body metabolises slowly. Used for the production of cough syrups, toothpastes and other oral hygiene products, cosmetics, paints, cigarettes and baked food items.
Publication: April 2020
Section: Pula/Imvula



