March 2018
Mr Cosmas Dumezweni Xaba (50) is a family man with a wife, seven children and one grandchild. He retired from the mines in 2008 and started to farm at Madzikane (KwaZulu-Natal), growing crops and rearing livestock. He strongly believes in doing things for the well-being of his family. He is a pastor at a local church and is also quite influential in local agricultural community development programmes.
Xaba owns ten cattle and 53 sheep and uses 3 ha to grow most of his food, which include spinach, potatoes, beans as well as maize. He sells excess produce locally and provides temporary employment to support the efforts of his family members.
He is supported in these efforts by a number of stakeholders including the Department of Agriculture, KWANALU and Lima RDF, an NGO that supports smallholder farmers with advice, and through a revolving loan fund, which supports his maize, broiler and potato production efforts.
His work with Kwanalu led to his co-operative being awarded a 1-row animal-drawn knapic planter through the DRDLR LandCare programme. His crop production and selling enterprises has allowed him to buy a bakkie that he now uses to deliver orders around the area. In the 2015/2016 season, for example, he had a turnover of R8 050 from his potatoes.
The need for financial capital for Xaba’s enterprises is significant, which led him to join a village level savings group initiated by Mahlathini Development Foundation and Strategic Action (a micro finance collaboration). The group was established in March last year and will be used as a financial institution for his enterprises. He recently took a loan from the group in an attempt to source a maize thresher that will help him to reduce hours of work shelling maize manually.
He is currently the chairperson of a farmer association through Kwanalu and a local facilitator for the Grain SA Farmer Innovation Programme (FIP) for smallholder farmers, implemented in Madzikane in collaboration with Kwanalu.
Xaba has been exposed to practices such as minimum tillage, improved seeds and a range of agro-chemicals through collaborative work with Pannar. He has tried minimum tillage for a couple of years and has witnessed an increase in land production potential and efficient use of inputs, saving both labour and money.
However, he was not familiar with the other conservation agricultural (CA) principles and practices, such as increased diversity (e.g. through intercropping) and permanent organic soil cover. He was eager to try this out with various planting methods and implements, with a view of comparing it with his normal mono-cropping practice.

His CA trial
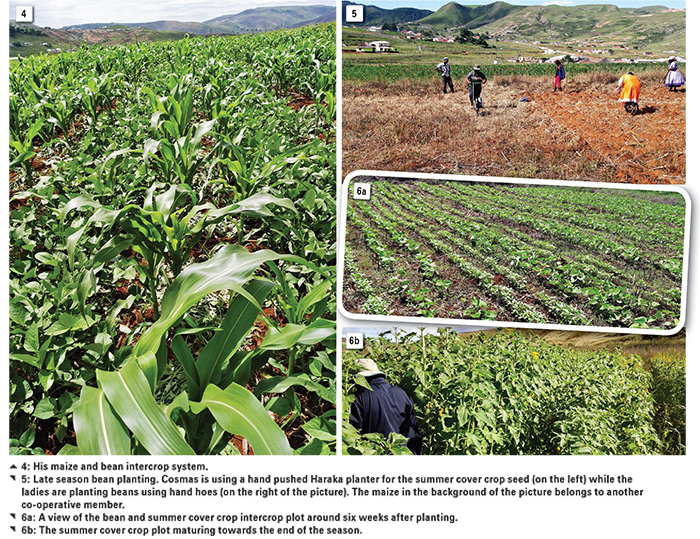
Xaba’s 400 m² plot was planted on 22 November 2016 using Sahara yellow maize seed, gadra beans and cowpea seed varieties, planted as tramline intercrops – thus, two rows maize and two rows legumes.
The learning group members worked together to lay out the plot, add lime and fertiliser and plant the basins and rows. This process was then continued for the other members of the group when they planted their own trials. Crop germination was not great, due to crows eating planted seeds. Subsequent growth, however, was good.
On 1 February last year, the learning group gathered again at Xaba’s field for a second round of planting trials. They wanted to experiment with late season planting of beans to compare that with early season planting and with planting of cover crops. They planted the following three trial plots:
Crop yields
He realised a somewhat low maize yield of 1,3 t/ha in his first year’s CA trial plot which has been planted with hand held planters. Damage by crows after planting was substantial on this plot that also had poor emergence of 53%. His maize CA plot planted with a tractor-drawn two-row no-till planter had good germination and yielded 3,6 t/ha. He sold his surplus maize locally in the village and made an income of around R2 400.
Conclusion
Agriculture has an important role to play in rural livelihoods to promote food security and income generation, but many challenges still exist despite the presence of support organisations. Stakeholder platforms for collaborative efforts and shared learning have a better chance of strengthening the smallholder sector. Moreover, communities should be at the centre of dialogue and decisions taken as they continue to research new options to strengthen their rural livelihoods.
The Grain SA FIP will continue to involve more smallholder farmers in the area after having witnessed the positive outcomes of crops grown under CA. Awareness events, such as farmers days, are a great medium for sharing and informing people about CA and its benefits.
Innovative farmers, such as Xaba, supported by learning groups and concerted collaborative efforts from interested and caring stakeholders in communities, have a big role to play in improving smallholder farming.
Publication: March 2018
Section: On farm level