Julie 2018
94
Does our insect resistant
management strategy still work?
G
enetically modified maize expres
sing the Bt gene, is planted in
South Africa to control one of the
most important insect pests of
maize, the African maize stemborer,
Bus-
seola fusca
(Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). This
specie has been reported to be resistant to
the first generation Bt maize (Bt 1) at several
localities in South Africa.
However, no resistance to the second
generation Bt maize (Bt 2) planted in South
Africa has been reported to date. The urgent
need to evaluate different African maize
stemborer populations by comparing these
populations’ life parameters were recog-
nised by the ARC-Grain Crops in collabora-
tion with the North-West University.
Larvae of the African maize stemborer were
collected from a few localities across South
Africa where maize is being produced.
Feeding studies were conducted in which
these larvae were reared on plant tissue
of maize events expressing the single (first
generation Bt maize) and pyramid (second
generation Bt maize) proteins, to compare
the fitness to that of larvae surviving on the
non-Bt iso-hybrids.
In a previous article published in the
SA Graan/Grain
of June 2017 (
‘n Oorsig van
stamboorderpopulasies se weerstandsvlakke
teen enkel- en dubbelgeen Bt-mielies
), re-
sults of only larval survival and larval mass
were presented. With the current article, life
parameter results of pupae (
Photo 1
) and
moths (
Photo 2
) are presented.
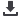
The pupation percentage of each location
was determined. The highest pupation
percentages were recorded for the non-
Bt treatment from the Ventersdorp popu-
lation (39,2%) followed by Venda (30%),
Potchefstroom (26,4%) and Grootpan (26%)
(
Graph 1
).
Pupation on the single Bt event was less
successful and the Potchefstroom popula-
tion had the highest pupation percentage
of 19,6% (Graph 1). No pupation occurred
in the Venda population on the Bt 1 treat-
ment, indicating that this population is still
highly susceptible to Bt maize. No larvae of
any populations survived on the Bt 2 treat-
ment and therefore no pupal data could be
recorded.
On farm level
African stemborer / Life parameters
Integrated pest control
Dr Annemie Erasmus
and
Elrine Strydom,
ARC-Grain Crops, Potchefstroom
Graph 1: Pupation (%) of different
Busseola fusca
populations after larval feeding on
non-Bt and Bt maize.
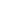
Graph 2: Mass of male and female pupae of different
Busseola fusca
populations feeding
on non-Bt and Bt maize.
1
2
1:
Busseola fusca
pupae.
2:
Busseola fusca
moth.