118
Depreciation of an asset commences when the asset is available for use as intended by man-
agement. Depreciation is charged to write off the asset’s carrying amount over its estimated
useful life to its estimated residual value, using a method that best reflects the pattern in which
the asset’s economic benefits are consumed by the organisation.
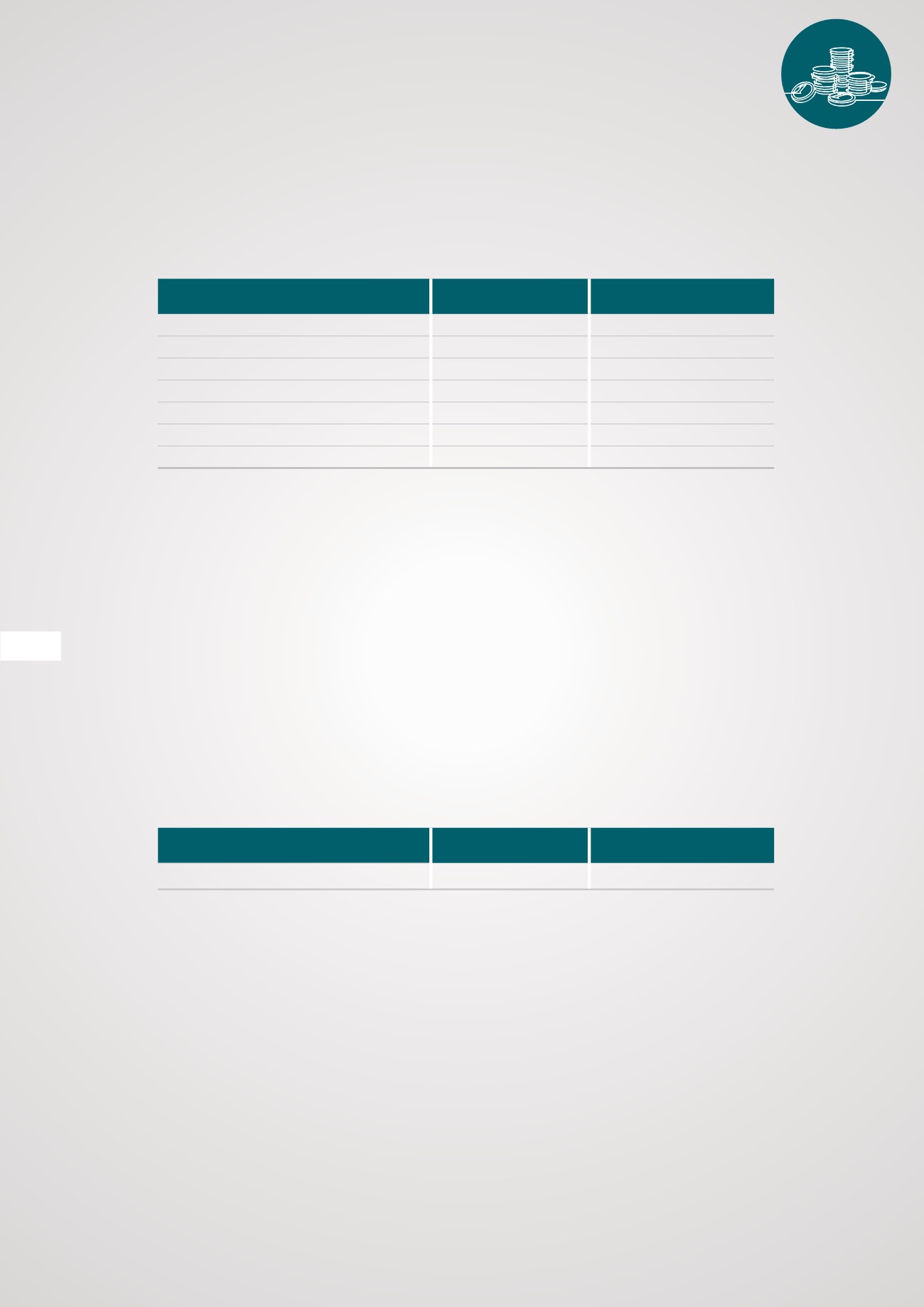
The useful lives of items of property, plant and equipment have been assessed as follows:
ITEM
AVERAGE USEFUL LIFE DEPRECIATION METHOD
Land and buildings
0 - 10%
Straight line
Plant and equipment
20%
Straight line
Motor vehicles
20%
Straight line
Furniture and fittings
20%
Straight line
Catering and other equipment
20%
Straight line
Office equipment
20%
Straight line
IT equipment
20%
Straight line
When indicators are present that the useful life and residual values of items of property, plant
and equipment have changed since the most recent annual reporting date, they are reassessed.
Any changes are accounted for prospectively as a change in accounting estimate.
Impairment tests are performed on property, plant and equipment when there is an indicator that
they may be impaired. When the carrying amount of an item of property, plant and equipment is
assessed to be higher than the estimated recoverable amount, an impairment loss is recognised
immediately in profit or loss to bring the carrying amount in line with the recoverable amount.
An item of property, plant and equipment is derecognised upon disposal or when no future eco-
nomic benefits are expected from its continued use or disposal. Any gain or loss arising from the
derecognition of an item of property, plant and equipment, determined as the difference between
the net disposable proceeds, if any, and the carrying amount of the item, is included in profit or
loss when the item is derecognised.
2.6 INTANGIBLE ASSETS
Intangible assets have a finite useful life and are carried at cost less accumulated amortisation and any
accumulated impairment losses. Amortisation is calculated using the straight-line method to allocate
the cost of intangible assets over their estimated useful lives as follows:
ITEM
AVERAGE USEFUL LIFE DEPRECIATION METHOD
Computer software
33%
Straight line
2.7 FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS
Initial measurement
Financial instruments are initially measured at the transaction price (including transaction costs
except in the initial measurement of financial assets and liabilities that are measured at fair value
through profit or loss) unless the arrangement constitutes, in effect, a financing transaction, in which
case it is measured at the present value of the future payments, discounted at a market rate of
interest for a similar debt instrument.
Financial instruments at amortised cost
These include trust funds, cash and cash equivalents, trade and other receivables and trade
and other payables. Those debt instruments which meet the criteria in section 11.8(b) of the
standard are subsequently measured at amortised cost using the effective interest method.
Debt instruments which are classified as current assets or current liabilities are measured at the
undiscounted amount of the cash expected to be received or paid, unless the arrangement
effectively constitutes a financing transaction.
FINANC
IAL
STATEMEN
TS
Basi
s of
p
re
parati
on and
sum
mary of significant
acco
unting
pol
icie
s (conti
nued
)